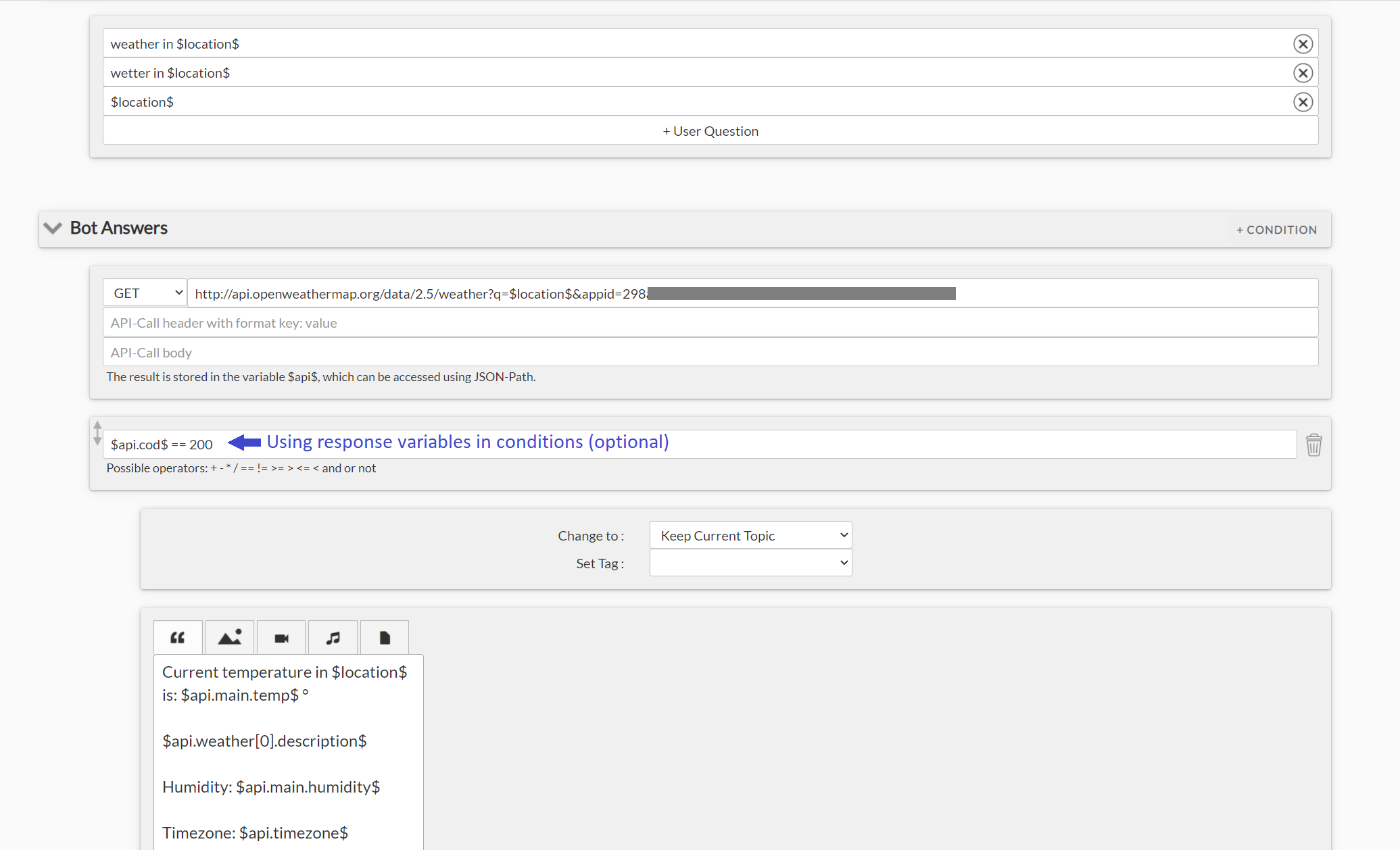
The Chatbot can perform a webservice (API) call to an external system from within a dialogue for retrieving additional data.
If you would like to use this functionality, please contact our support ([email protected]). When the module is activated, an additional field for the URL (endpoint) of the target system appears in the detailed view of a dialogue. Furthermore there will be a field where you can choose the classical REST methods like GET, PUT, POST, DELETE for the call.
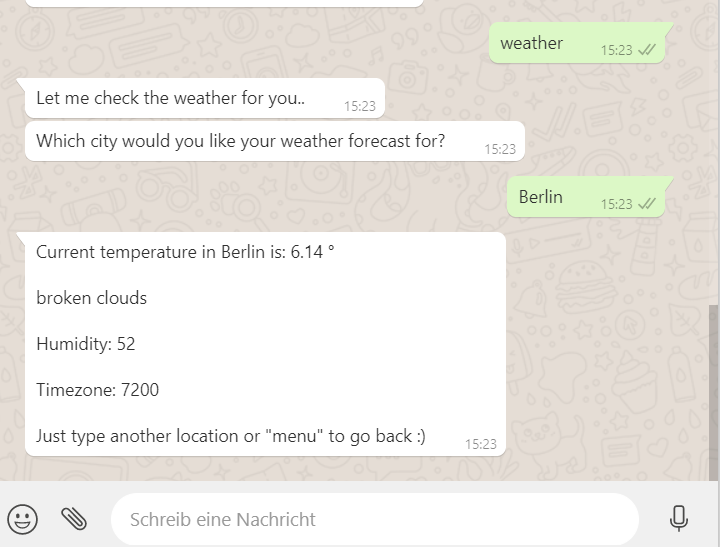
In our example, we are performing a request to a weather service for retrieving the current weather. The variable $openweather$ holds the desired place that the user wants to get the weather info for.
This is how the API response looks like:
{
"coord": {
"lon": -0.13,
"lat": 51.51
},
"weather": [
{
"id": 500,
"main": "Rain",
"description": "light rain",
"icon": "10d"
}
],
"base": "stations",
"main": {
"temp": 10.68,
"pressure": 996,
"humidity": 87,
"temp_min": 9.44,
"temp_max": 11.67
},
"visibility": 10000,
"wind": {
"speed": 3.1,
"deg": 120
},
"clouds": {
"all": 75
},
"dt": 1556174048,
"sys": {
"type": 1,
"id": 1414,
"message": 0.0109,
"country": "GB",
"sunrise": 1556167474,
"sunset": 1556219532
},
"id": 2643743,
"name": "London",
"cod": 200
}
You can use JSON-Path for printing the API response to the bot-answer, e.g. $api.main.temp$ for the temperature. $api$ holds the JSON-Object of the response.
This is how the whole thing looks like in action:
You can also use the response in if-else conditions, for example for reacting on errors (e.g. just like in the above example, the text response will be returned only in case of success, $api.cod$ == 200).
Using special syntax you can save values from the API response to variables and make them available for further use: $temperature=($api.main.temp$)$ where $temperature$ is the variable the value should be saved to and $api.main.temp$ is the value of the response.
Note: For debugging purposes you can output the call made by the bot using a variable $api_request$.